Introduction to Fleet Management
Fleet Management Definition
Businesses across all sectors depend on commercial vehicles to transport people and products daily from cross-country delivery services to your neighborhood gas and oil provider. These commercial vehicles are called fleets and are often one of the most expensive assets for a business.
Fleet management is the process of organizing, coordinating, and overseeing company vehicles. Fleet management includes maintenance, acquiring vehicles, managing drivers, tracking vehicle movements, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
In this detailed guide, discover everything you need to know about fleet management and why it is vital for businesses in the world today.
Let’s dive in!
Evolution of Fleet Management

Advances in technology have revolutionized fleet management. Even with these advancements, innovations are still emerging each year.
Here are the new trends in technologies that continue to impact fleet management practices:
- Autonomous vehicles: I am sure you have already seen autonomous vehicles used in military applications or niche logistics. These integrated devices depend on various components in a fleet management system that provides efficiency and safety.
- 5G network connectivity: Most wireless carriers have already introduced 5G connectivity, which is 100 times faster than 4G technology. These fast speeds improve the hardware used for fleet management and the bandwidth used for the Internet of Things (IoT).
- Telematics: With telematics, operators can display real-time vehicle diagnostics that help to enhance efficiency and decision-making. Technologies like artificial intelligence continue to enhance these capabilities to become more attractive and allow new visualizations and data collection standards.
- Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS): Mobility-as-a-service is enabled by various major trends such as the rise of subscription services and the sharing economy. MaaS can lead to cost-minimization of transport services like public transportation, rental, and sharing offerings.
In response to changing business needs, fleet management has undergone significant changes. These technologies have been a major catalyst for the evolution of fleet management.
How Fleet Management Works

A fleet management system coordinates and controls a group of vehicles used to transport goods to ensure efficiency and safety.
For this system to work properly, a government body or a business entity must establish clear expectations and set standardized practices.
A fleet management system involves a set of activities and functionalities that collaborate to manage a fleet of vehicles.
Below are some of the core functionalities of a fleet management system:
Real-Time Vehicle Tracking
Fleet management systems use telematics and GPS technology to track and monitor vehicles in real time. Telematics collect and transmit vehicle speed, mileage, and fuel consumption data, while GPS allows precise location tracking.
Data Analytics

This involves the collection of data reports from various fleet performance metrics, such as vehicle utilization, fuel consumption, and maintenance costs. This data helps in identifying areas for improvement, optimizing operations, and making data-driven decisions.
Vehicle Status Monitoring and Management System

The system collects and displays information about vehicle status, such as engine health, fuel levels, and maintenance needs. It also maintains a database of vehicle details like vehicle specifications, ownership, registration, and insurance information.
Driver Management

With a driver performance monitoring system, you can track driver behavior, such as speeding, harsh braking, and acceleration. It helps in promoting safer driving practices and reducing breakdowns.
These core components enable businesses to manage their fleet, enhance operations, monitor vehicle performance, and make informed decisions based on data-driven insights.
Benefits of Fleet Management
Operational Efficiency
Businesses can implement numerous strategies to streamline workflows to enhance operational efficiency in fleet management.
One of the strategies to consider is adopting robust fleet management software, which enables businesses to automate and streamline fleet-related processes.
The software centralizes data, provides real-time information, and automates tasks. By eliminating manual processes, businesses can achieve greater operational efficiency.
Route planning is another strategy that reduces mileage and fuel consumption while boosting productivity. With this strategy, you can optimize routes by analyzing historical data, considering real-time traffic information, and using algorithms.
By integrating telematics technologies, fleet management software organizations can gain valuable insights into their fleet operation. This data identifies inefficiencies, optimizes maintenance schedules, and improves productivity.
Controlling Costs

Cost-controlling mechanisms provide businesses with the required tools and insights to manage and reduce costs.
Mechanisms such as fuel card integration will help businesses track fuel purchases and monitor fuel expenses. This integration also helps detect discrepancies or unauthorized fuel usage, thus controlling costs.
Another cost-controlling mechanism is data analytics. By analyzing data, fleet managers can identify cost-saving areas, make data-driven decisions, and implement strategies to optimize fleet efficiency.
Fleet management software is also another mechanism. FMS assists organizations in monitoring regular inspections, repairs, and maintenance schedules on your vehicles. With careful maintenance management, fleet managers can prevent costly breakdowns and reduce the chances of repairs.
Various strategies and practices exist to reduce operational expenses while managing a fleet of vehicles.
By implementing these strategies, businesses can improve their financial performance, minimize waste, and ensure effective allocation of resources for better results.
Factors to Consider
The following are the best strategies and practices for managing fleet operational expenses to consider:
- Emphasize driver training and safety: Prioritizing training on safe driving practices significantly impacts fleet expenses. Often, well-trained drivers have fewer accidents, leading to lower insurance premiums and reduced vehicle repair costs.
- Implement fuel management practices: Fuel expenses are a significant factor that affects fleet costs. Implementing effective fuel management practices can help control fuel consumption. Using fuel cards, monitoring fuel usage, and leveraging data analytics are strategic practices that can lead to significant fuel savings.
- Leverage technology for expense tracking and analysis: Using technology makes fleet expense monitoring easier. Fleet managers can make data-driven decisions by implementing expense monitoring tools and software solutions, which enable them to track and analyze expenditures in real time.
- Track key performance indicators (KPIs): When assessing the effectiveness of management strategies, it is essential to track and analyze key performance indicators (KPIs). Some KPIs include driver behavior, vehicle utilization, and accident rates. Regularly monitoring these metrics allows fleet managers to manage expenses and reduce costs.
Improving Fleet Management

Continuous improvement is key for optimizing fleet management and achieving better outcomes. Here are some strategies for improving fleet management:
- Set clear objectives: Define clear and specific objectives for your fleet management operations. Your objective should be to reduce fuel consumption, improve driver safety records, or decrease maintenance costs.
- Embrace technology: Adopt fleet management software and telematics systems to streamline operations and gather valuable data. These technologies provide insights into vehicle location, fuel consumption, and maintenance requirements. For continuous improvement, use the data to identify inefficiencies, monitor vehicle health, and make informed decisions.
- Fleet maintenance program: Develop a comprehensive fleet maintenance program that includes regular inspections, preventive maintenance schedules, and immediate repair procedures. By implementing maintenance programs, you can prevent breakdowns and expensive repairs.
- Benchmarking: Compare your fleet management operations with industry benchmarks. Research and learn from other successful fleet management organizations. Attend industry conferences, join professional associations, and seek networking opportunities and knowledge sharing. Benchmarking helps identify areas where you can improve and adopt proven strategies.
Emerging Technologies

Adapting to emerging technologies is vital for staying competitive and maximizing the benefits of fleet management.
One of the ways to adapt to new technologies and industry practices is to update yourself with the latest trends in fleet management. Subscribe to industry publications and attend webinars and conferences to stay informed about new trends and innovations.
Another way to embrace new technology and practices is to collaborate with technology providers. Establish relationships with tech providers who specialize in fleet management solutions. Engage them in discussions to understand their offerings, customization options, and ongoing support.
Moreover, consider the integration requirements of new technologies with your fleet management systems and workflows. Examine the need for additional hardware, software, or infrastructure upgrades.
Lastly, develop a robust implementation plan that includes training programs to ensure employees can utilize the technology and adapt to new practices.
Fleet Management Components
Fleet Management System

A fleet management system helps organizations manage their fleets of vehicles effectively. It provides current data to optimize operations, reduce costs, and improve safety.
FMS is hardware devices such as GPS trackers, fuel sensors, and onboard diagnostics that collect data from fleet vehicles.
After collection, the gathered data is transmitted to the central system through cellular networks or satellite communication.
The system processes and stores the received data in a secure database where fleet managers can gain access to it, generate reports, and manage operations.
Managing a fleet of vehicles involves the interplay of several core components that work together to ensure efficient operations.
The following are core components in managing a fleet of vehicles:
- Vehicle acquisition: The acquisition of vehicles is selecting the right vehicle types, negotiating purchase agreements, and ensuring compliance with regulations and company policies.
- Fuel management: Managing fuel consumption is crucial for controlling costs and reducing environmental impact. Activities such as monitoring fuel usage and fuel expenses can help reduce fuel consumption, lower costs, and promote sustainability.
- Safety and compliance: Ensuring safety and compliance with regulations such as safety policies and driver safety practices can lead to the well-being of drivers, reduce liability risks, and maintain a positive reputation.
Fleet Management Software

Fleet management software can track vehicles, improve driver safety, optimize routes, and use data in strategic decision-making.
The rise in technology has resulted in more complex fleet management software than ever.
Businesses that need to increase efficiency and streamline their operations must have the right fleet management software.
Below are some of the specialized software solutions tailored for fleet management:
- Fleetio: With Fleetio, you can monitor your maintenance workflow, manage work orders, and integrate with third-party services. This software also provides notifications and automated schedules for timely fleet upkeep.
- Circuit for teams: This software enables fleet managers to optimize routes and simplify communication with mobile app features such as advanced route planning and batch editing stops for delivery models.
- Samsara: Safety is the first element that defines Samsara. It utilizes dashcams and driver behavior metrics to improve road safety. Samsara integrates ELD compliance, real-time tracking, and proactive notifications to encourage careful driving practices.
- Motive: By leveraging Motive, fleets can minimize costs and maintain regulatory compliance. Motive achieves this feat through integrating AI-based fuel management solutions and safety features.
- Onfleet: To reduce delivery times and operational costs, Onfleet offers tools that enhance real-time tracking, route planning, and automated communication systems.
The best software for fleet management understands the challenges fleet managers face daily.
Although most software solutions may succeed in one area or another, finding software that balances different needs can be overwhelming.
During my search for the best fleet management solutions, I found these three elements:
Fleet Management Solutions

Fleet management solutions refer to the comprehensive set of tools, technologies, and practices used to manage and optimize a fleet of vehicles.
These solutions aim to simplify operations, enhance safety, and lower costs associated with fleet management.
One of the fleet management solutions is an end-to-end tool. It covers the whole fleet lifecycle from vehicle acquisition to disposal. Typically, it entails a combination of software applications, hardware devices, and data analytics to allow businesses to make insight-driven decisions.
Fleet management solutions provide customization options to meet the diverse business needs of different industries and organizations.
These options enable businesses to tailor the fleet management solution to specific requirements, workflows, and industry regulations.
Here are the customization options available in fleet management solutions:
- Dashboard customization: The dashboard is the central interface of the fleet management software where users can access important information. Customization options enable businesses to configure the dashboard layout, widgets, and data visualization.
- Alerts and notifications: Fleet management solutions provide alerts and notifications to keep users informed about important events related to their fleet. Businesses can define specific triggers and thresholds for alerts with these customization options.
- Reporting and analytics: These capabilities provide insights into fleet performance and trends. Organizations can create customized reports and dashboards designed for specific metrics and KPIs. Users can select the data they want to include and apply filters that best represent the required information.
- Integration with third-party systems: Most businesses already use other software systems such as accounting, CRM, or ERP solutions. Customization options enable seamless integration between the fleet management solution and these existing systems. Integrating these systems provides a way for data exchange, automated workflows, and consolidated reporting.
Technology in Fleet Management
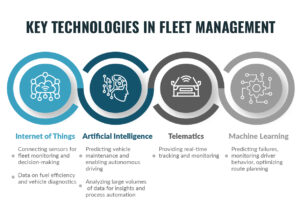
The fleet industry has evolved in recent years. Enabling businesses to improve efficiency, reduce costs, enhance safety, and optimize operations.
With the adoption of technologies like the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, telematics, and machine learning, fleet managers can effectively track, optimize, and maintain their fleets.
The IoT devices are transforming fleet management with the expectation to grow in the years to come. By connecting sensors and other assets to provide fleet monitoring and operational decision-making, an Internet of Things-powered system offers valuable data on fuel efficiency and vehicle diagnostics— leading to improved performance and cost savings
Integrating artificial intelligence algorithms with fleet management systems helps predict vehicle maintenance, enhancing fleets by enabling autonomous driving in the future. AI technologies analyze large volumes of data to provide insights and automate processes.
Machine learning algorithms analyze complex data patterns to predict failures and identify potential problems before they occur. ML can monitor driver behavior and safety, optimize route planning, and predict demand to improve fleet operations.
Telematics
In the modern digital era, businesses can no longer rely on guesswork and manual record-keeping. They must prioritize environmental responsibility, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Telematics emerges as a crucial tool in achieving these objectives.
Here is the role of telematics in modern fleet management:
Real-Time Tracking

Telematics systems enable fleet managers to track vehicles using GPS technology, allowing for accurate and up-to-date information about the location, speed, and status of all vehicles in the system. With real-time vehicle tracking, you can maximize routes, ensure safety, reduce fuel usage, and decrease journey time.
Vehicle Diagnostics
Telematics devices collect data such as engine performance, fuel consumption, tire pressure, battery health, and additional metrics. This data is then transmitted to fleet managers, providing information about the health and condition of each vehicle. Monitoring vehicle diagnostics, fleet managers can identify maintenance needs, detect potential issues, and schedule repairs accordingly.
Communication Capabilities

The use of telematics systems facilitates two-way communication between fleet managers and drivers. Managers send real-time instructions, updates, and alerts to drivers due to this instant communication.
Challenges of Fleet Management
Meeting Compliance Requirements

It is not unusual to encounter challenges when managing fleets, costs, drivers, and schedules. Although most software solutions and technologies eliminate some of these challenges for fleet managers, you will still need to solve issues quickly.
Navigating regulatory compliance in fleet management is vital for businesses to ensure adherence to legal requirements, maintain safety standards, and avoid penalties or legal issues.
However, there are strategies that businesses can employ to ensure compliance with both local and international standards. To meet compliance requirements, follow these strategies:
- Stay informed: Stay updated with new local and international regulations that apply to fleet management. Regularly monitor industry publications and government websites to stay informed about regulation modifications or updates.
- Conduct compliance assessments: Perform regular compliance assessments to evaluate your current organization’s practices and identify any non-compliance gaps. Internal audits or external consultants with expertise in compliance and standards can help achieve this. Areas that require assessments include driver qualifications, vehicle maintenance, service hours, record-keeping, and other relevant compliance requirements.
- Training and education: Provide training programs for employees at all levels to ensure awareness of the compliance regulations. This practice includes training on specific standards, requirements, and policies relevant to their job functions.
- Engage legal and compliance experts: Seek advice and guidance from legal and compliance experts who are well informed in local and international standards. They usually offer informative insights, interpret sophisticated regulations, and assist in developing strategies to ensure compliance.
- Implement technology solutions: To help automate compliance processes, use technology solutions such as fleet management software and telematics systems. These solutions assess driver qualifications, monitor vehicle maintenance, record hours of service, and generate reports for compliance purposes.
Health and Safety
Addressing fleet management health and safety is essential in safeguarding the well-being of drivers, employees, and the general public. To enhance health and safety, below are some key considerations.
First, conduct a risk assessment of your fleet operations to identify possible health and safety hazards. Examine factors such as driver behavior, road conditions, and vehicle maintenance. Identify and prioritize the risks and develop plans to mitigate them.

Secondly, provide a thorough driver training program that covers safe driving techniques, defensive driving, and compliance with traffic laws. Include specific training on handling emergencies and harsh weather conditions.
Moreover, develop and enforce policies and procedures to manage driver fatigue. Ensure drivers comply with regulations regarding hours of work, rest periods, and breaks. Provide education and training on the importance of enough rest and sleep, and encourage drivers to monitor fatigue levels and report any concerns.
Fleet Manager Responsibilities
Roles and Responsibilities

Fleet managers work in the transportation industry as logistics experts. Their company’s responsibility is to manage every aspect of vehicles and drivers.
Apart from buying and maintaining delivery vehicles, fleet managers have other duties. The following are some of the responsibilities of fleet managers.
- Recording data: Fleet managers are responsible for recording and maintaining accurate information about a fleet. They keep detailed records of every vehicle in their fleet.
- Analyze recorded data: By analyzing recorded data, fleet managers can reroute vehicles or change travel schedules when necessary. Drivers can find routes with fewer road hazards or traffic to save travel time.
- Select the right vehicles: Fleet managers determine the best financial strategy to build a fleet. Once a fleet vehicle has reached the end of its useful life and is ready to be resold, fleet managers are adept at selling it for the highest possible price.
Other responsibilities of fleet managers include:
- They manage accident reports
- Creating and managing fleet policies
- Use GPS systems to find vehicle locations
- Seek ways to lower costs and increase profits
When managing a team of drivers and stakeholders, possessing leadership skills is crucial. As a fleet manager, you must delegate tasks, communicate effectively, provide clear direction, and encourage your team to work towards a common goal.
A leader should have strong problem-solving skills to make tough decisions and take responsibility for the results of their decision.
Fleet managers with leadership skills can create a positive work environment, increase employee morale, and drive better results.
Optimizing Fleet Vehicle Management
Vehicle Acquisition

Vehicle acquisition means acquiring new vehicles for operational needs in a business. It directly impacts the day-to-day operations of a business.
Whether you are managing a fleet of service vehicles, delivery trucks, or forklifts, selecting the appropriate vehicle acquisition process can result in improved performance, cost savings, and a favorable image.
When it comes to vehicle procurement, the acquisition of vehicles is a key aspect that can impact costs and fleet performance.
For cost-effective and strategic vehicle procurement, consider the following strategies:
- Need assessment and right-sizing: Conduct an in-depth needs assessment to determine the exact requirements of your fleet. Consider factors such as the nature of operations, payload capacity, fuel efficiency, maintenance costs, and driver preferences. By right-sizing your fleet, you can avoid unnecessary purchases and ensure each vehicle meets your organizational needs.
- Total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis: Factors in TCO analysis include fuel consumption, repair costs, insurance premiums, depreciation, and resale value. Analyze and compare different vehicle brands to identify the best long-term value and lowest TCO offer.
- Standardization and consolidation: Standardize your fleet by limiting your selection of vehicle models. This standardization allows for easier inventory management and potential training and diagnostic equipment savings. Consolidating your fleet with a single supplier or several suppliers can give you leverage for negotiating better pricing and service agreements.
- Leasing and financing options: Instead of procuring vehicles outright, consider leasing them. Leasing provides flexibility and lower upfront costs. Evaluate various lease terms, mileage allowances, and end-of-lease options to find the best fit for your fleet.
Optimizing Vehicle Maintenance

Organizational profitability depends on proactive maintenance of its vehicle fleet to prolong its life, improve efficiency, and enhance longevity.
Proactive maintenance helps identify and address potential issues before they become problems. By addressing minor repairs immediately, you can prevent costly breakdowns, reduce vehicle downtime, and avoid expensive replacements.
Improving the performance and lifespan of a fleet vehicle requires a systematic and comprehensive approach.
Conducting regular inspections is one of the approaches. It ensures the functionality of critical safety systems such as brakes, tires, lights, and steering. Regularly inspecting vehicles reduces the risk of accidents caused by equipment failures and enhances the safety of your drivers, passengers, and other road users.
Vehicles that undergo proactive maintenance are more reliable. You can minimize unexpected breakdowns and reduce mechanical failures by identifying and resolving issues early on.

There are two main approaches to vehicle maintenance: scheduled maintenance and reactive repairs. Scheduled maintenance involves planned and routine maintenance activities performed based on specified criteria. On the other hand, reactive repairs are in response to a specific issue or unexpected failure that has occurred in the vehicle.
The purpose of scheduled maintenance is to prevent potential issues, ensure optimal vehicle performance, and extend the lifespan of the vehicle.
On the other hand, reactive repairs are unplanned and often caused by equipment malfunctions, component failures, or accidents.
Fuel Management

Fuel costs represent a significant portion of fleet operating expenses, making fuel management a crucial component of efficient fleet management.
For effective fuel management, follow these practices:
- Invest in fuel-efficient vehicles: Focus on building your fleet around vehicles designed for fuel efficiency. These include hybrids, electrics, or newer models with advanced technology for better mileage.
- Implement fleet management software: Many fleet management software systems provide features to track and manage fuel usage and provide helpful data pinpoint areas to enhance efficiency.
- Train drivers on fuel-saving techniques: Said techniques include reducing rapid acceleration and deceleration, minimizing idle time, and maintaining a constant speed when possible.
- Use GPS for route planning: Leveraging a GPS can help to lower unnecessary driving by finding the shortest and quickest routes.
- Use Fuel Cards: These allow for easy fuel usage tracking and expenditure. Most of these fuel cards offer rewards and discounts.
A significant aspect of fleet management is monitoring and optimizing fuel consumption. Here are some optimization opportunities to help you monitor fuel consumption:
- Gather historical fuel consumption data for your fleet. You can obtain this data from fuel purchase records, fuel card usage, or telematics systems. Establish a baseline by analyzing fuel consumption patterns across various vehicles, drivers, and routes.
- Track fuel consumption metrics to monitor fuel consumption on an ongoing basis. To achieve this, utilize fleet management software or tools. Track metrics such as gallons/liters consumed per mile/kilometer, fuel economy (MPG or L/100km), and fuel cost per mile/kilometer.
- Set fuel consumption goals and KPIs for your fleet. Include reducing fuel consumption by a percentage, improving fuel economy ratings, or attaining a specific fuel cost per mile/kilometer target.
How to Find a Fleet Management Company
Choosing the Right Partner

When selecting a fleet management company, explore different criteria to ensure you choose the right partner that aligns with your needs and goals.
Consider these criteria below:
- Industry reputation: Research the reputation of the fleet management company. Look for information about their standing, recognition, and any awards or certifications they have received. Industry publications, forums, and associations are key sources to obtain knowledge concerning their reputation.
- Client testimonials: Request testimonials or references from current or previous clients of the fleet management company. Reach out to these clients and gather their feedback and experiences working with the company. Client testimonials provide firsthand information about company performance and customer satisfaction.
- Track record: Look at a fleet management company’s history of successful engagements, the duration of their client relationships, and their ability to deliver on commitments. Find out their experience in managing fleets in terms of size, industry, and operational complexity. A strong track record indicates an ability to consistently meet client expectations and seamlessly navigate the challenges of their clients
- Experience and expertise: Look for a fleet management company with industry knowledge, understanding of regulatory requirements, and familiarity with the specific challenges of your fleet operations.
- Technology and innovation: Look for advanced fleet management systems, telematics platforms, and digital solutions that enhance efficiency, optimize routes, monitor driver behavior, and provide real-time data. Evaluate their ability to integrate with your existing systems and adapt to future technological advancements.
- Financial stability: Evaluate the financial stability and strength of the fleet management company. Explore their financial history, profitability, and long-term viability. A financially stable partner is more likely to invest in the necessary resources and consistently support your needs.
Conclusion
In summary, fleet management encompasses fleet maintenance, vehicle acquisition, driver management, tracking, and regulatory compliance.
For the fleet management system to work, a government or a business entity must set standardized practices or establish clear expectations
In response to business trends, fleet managers should fully embrace new technological advancements to stay updated and on the curve. These technologies and practices are crucial for fleet management:
Ultimately, businesses can improve efficiency, reduce costs, enhance safety, and optimize operations by adopting cutting-edge technologies!